Infection or Inflammation? The Differences and Treatment Options
The concepts of infection and inflammation are often confused, yet they fundamentally refer to different biological processes. Both are the body’s response to harmful effects, whether from microorganisms, chemicals, or physical injury. In the case of infection, pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi enter the body and proliferate, while inflammation is part of the body’s defense mechanism that develops as a consequence of injury or infection.
Inflammation is the body’s natural reaction aimed at removing harmful substances, regenerating damaged tissues, and protecting against infections. During inflammatory processes, blood circulation increases, white blood cells are activated, and various biological substances are released to aid healing. In contrast, infection is generally a more chronic condition that requires longer treatment and can lead to more serious complications if not properly managed.
Understanding these two concepts is essential for consciously addressing our health and the body’s reactions. Below, we will examine in more detail the differences between infections and inflammations, as well as their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Infections: The Impact of Pathogens on the Body
Infection is the process by which pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, enter the body and begin to multiply. The most common sources of infections can be air, water, food, and direct contact through the skin. Infections can take various forms, such as respiratory, gastrointestinal, or skin infections.
The initial signs of infection are usually associated with the activation of the body’s defense mechanism, leading to the onset of inflammatory reactions. The immune system’s white blood cells begin to fight against the pathogens, which can result in symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and other signs.
The symptoms of infections can vary and depend on the area attacked by the pathogen. For example, respiratory infections, such as colds or flu, can cause coughing, sore throat, and fever, while gastrointestinal infections can lead to diarrhea and nausea.
Infections are typically treated with antibiotics, antiviral agents, or antifungal medications, depending on the type of pathogen causing the illness. However, it is crucial that treatment is always prescribed by a doctor, as improper use of medication can have severe consequences, including the development of resistant pathogens.
To prevent infections, it is important to maintain proper hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, receiving vaccinations, and following a balanced diet that strengthens the immune system.
Inflammation: The Body’s Defense Mechanisms
Inflammation is the body’s response to injury or infection, which is part of the natural defense mechanisms. The aim of the inflammatory process is to remove harmful substances and regenerate tissues. Inflammation can be acute or chronic, depending on how long it lasts.
Acute inflammation occurs suddenly and usually lasts for a short period. The most common causes include infections, physical injuries, or the effects of chemicals. During acute inflammation, the body reacts quickly, and the goal of inflammatory responses is to kill pathogens and restore damaged tissues.
Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, lasts longer and may not be directly related to infection. It can often occur as a result of autoimmune diseases, allergies, or other chronic conditions. Chronic inflammation can lead to numerous health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic illnesses.
Symptoms of inflammation include swelling, redness, pain, and increased temperature. Treatment for inflammation typically involves the use of anti-inflammatory medications, but it is essential that treatment is prescribed by a doctor, as long-term use of anti-inflammatory drugs can negatively affect the body.
It is important to note that while inflammation is a natural part of the healing process, if inflammation becomes chronic, medical intervention may be necessary to prevent further issues.
The Differences Between Infection and Inflammation
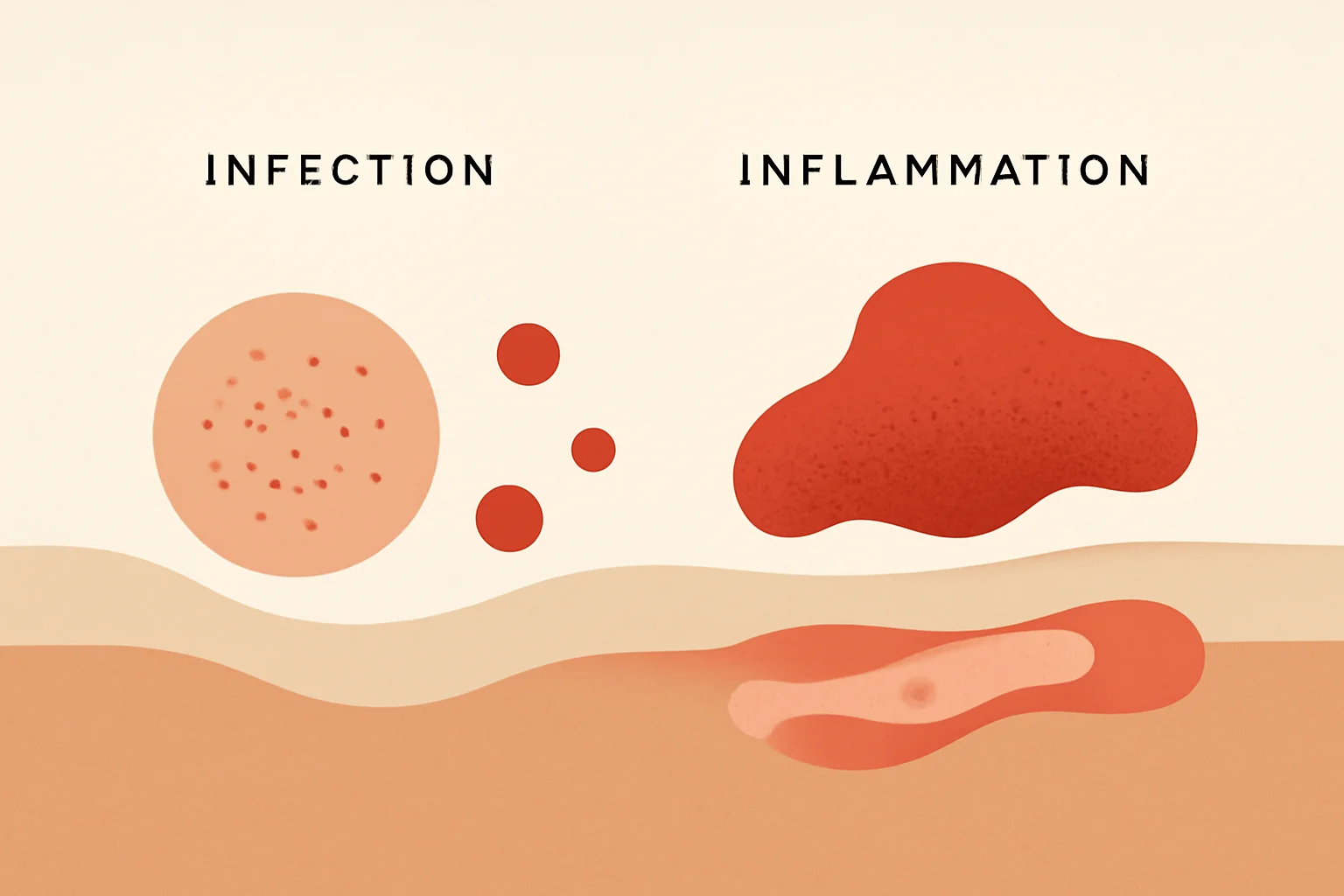
The primary difference between infection and inflammation lies in the triggering cause and the nature of the process. Infection always involves some pathogen, such as bacterial, viral, or fungal attack, while inflammation is the body’s response to harmful effects, which can result from infection, injury, or irritation.
Infection is associated with the proliferation of pathogens, which can often lead to complications if not treated promptly. In contrast, inflammation is a protective mechanism aimed at safeguarding the body from harmful effects and facilitating healing.
The symptoms also differ: while infection is characterized by symptoms caused by pathogens, inflammation is marked by inflammatory reactions such as pain, swelling, and redness.
During diagnosis, doctors consider symptoms, medical history, and conduct various tests to determine the exact cause. The treatment for infections and inflammations can differ, making accurate diagnosis crucial.
A healthy lifestyle, proper hygiene practices, and regular medical check-ups can help prevent infections and inflammations.
Understanding infection and inflammation is essential for consciously managing our body’s reactions and seeking appropriate medical care.
**Warning:** This article does not constitute medical advice. In case of health problems, always consult a doctor.