Fungal infection or eczema? Symptoms, causes, and effective treatment methods
The skin fungus and eczema are two common skin problems that complicate the lives of many people. These skin diseases have different symptoms and causes, which can often be confusing in terms of diagnosis and treatment. Skin fungus, caused by fungal infections, typically appears on the skin, hair, or nails, while eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, often develops as a result of allergic reactions, environmental factors, or stress.
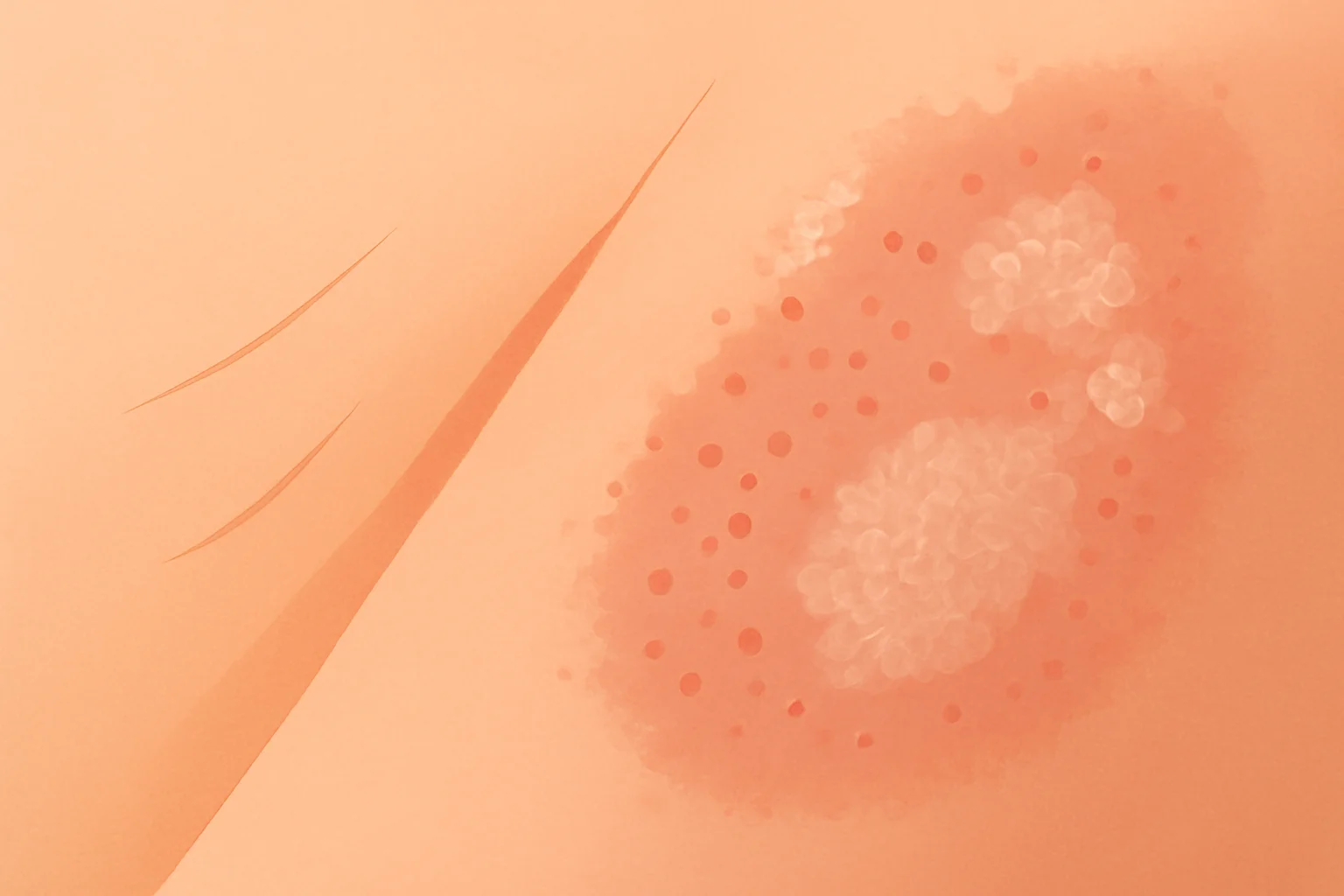
In both conditions, skin irritation and inflammation can be observed, leading to itching and discomfort. Skin fungus usually appears in the form of red, scaly patches, while eczema can be associated with dry skin, flaking, and redness. Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, as the treatment methods for the two conditions require completely different approaches.
Skin Fungus: Symptoms and Causes
Skin fungus, caused by a fungal infection, can appear on various areas of the skin, such as the feet, nails, or scalp. Fungal infections are most commonly caused by fungi belonging to the genera Candida, Trichophyton, and Microsporum. These fungi are naturally present on the skin, but certain factors such as moisture, temperature, and a weakened immune system can contribute to the development of the infection.
The symptoms of skin fungus typically manifest as follows:
1. **Itching**: One of the main discomforts of skin fungus is the itching, which can be intense in the infected area.
2. **Red Patches**: The skin affected by the fungal infection may be covered with red, inflamed patches.
3. **Scaling**: Signs of peeling and scaling of the skin may also appear in the affected area.
4. **Ulcers**: In more severe cases, ulcers may develop, which can be painful.
The development of skin fungus can be influenced by several factors. The most common causes include excessive sweating, wearing tight clothing, skin injuries, and a weak immune system. Environments where the skin remains continuously moist, such as in swimming pools or saunas, also increase the risk of developing skin fungus.
The treatment of skin fungus typically involves the use of antifungal creams or medications. Proper diagnosis is important, as treatment methods may vary for different fungal infections.
Eczema: Symptoms and Causes
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that is particularly common in childhood but can also occur in adults. The exact causes of eczema are not completely understood, but genetic predisposition, allergic reactions, and environmental factors can all contribute to the development of the disease.
The symptoms of eczema generally manifest as follows:
1. **Itching**: The most characteristic symptom of eczema is itching, which can often be bothersome and cause sleep disturbances.
2. **Dry Skin**: The affected areas of skin are often dry and flaky, which can lead to further irritation.
3. **Redness and Inflammation**: The skin surfaces affected by eczema may be red and inflamed.
4. **Scaly Patches**: Scaly, peeling patches may also appear on the skin, particularly on the elbows, knees, and neck.
The triggers for eczema encompass a wide range. In addition to genetic predisposition, environmental factors such as pollen, dust, irritating chemicals, or even food allergies can play a role in the manifestation of the disease. Stress can also exacerbate symptoms, making the maintenance of mental health important during treatment.
The treatment of eczema typically involves the use of moisturizing creams and anti-inflammatory ointments. Avoiding allergens, managing stress, and following medical advice can also contribute to alleviating symptoms.
Skin Fungus and Eczema: Differences and Similarities
Although skin fungus and eczema share several similarities, such as itching and skin irritation, it is important to understand the differences between them. Skin fungus is a fungal infection, while eczema is an inflammatory skin disease caused by allergic reactions, genetic predisposition, or environmental factors.
Skin fungus typically appears as well-defined, red, scaly patches, while eczema often affects larger areas of skin and is associated with dryness and flaking. The symptoms of skin fungus usually appear suddenly, while the symptoms of eczema can develop more slowly and may be chronic in nature.
A medical examination is necessary for diagnosis, as the treatment for the two conditions is completely different. Antifungal agents are required for the treatment of skin fungus, while anti-inflammatory and moisturizing preparations are recommended for eczema.
The approaches to prevention also differ between the two conditions. For skin fungus, it is important to keep the skin dry and maintain proper hygiene practices, while preventing eczema involves avoiding potential allergens and keeping the skin moisturized.
Effective Treatment Methods
The treatment of skin fungus and eczema requires different approaches, and choosing the right treatment is crucial for alleviating symptoms. For skin fungus, antifungal medications such as creams, ointments, or tablets are the most common treatment methods. The effectiveness of the medications greatly depends on the type of fungus and the severity of the infection, so medical consultation is recommended before starting treatment.
The treatment of eczema typically involves the use of moisturizing creams and anti-inflammatory agents. Doctors often recommend proper hydration of the skin, which helps prevent dryness and worsening of symptoms. Additionally, antihistamines may help relieve itching.
Stress management is also an important part of eczema treatment. Relaxation techniques such as meditation, breathing exercises, or yoga can help reduce stress, thereby improving the condition of the skin.
For both skin fungus and eczema, it is important for patients to be informed about prevention options, such as maintaining hygiene practices, proper skincare, and avoiding allergens.
These treatment methods not only serve to alleviate symptoms but also help maintain the health of the skin.
Note: This article does not constitute medical advice, and in the case of health issues, everyone should heed their doctor’s advice.

