Eczema or Skin Fungal Infection? Learn About the Symptoms and Treatment Options!
The skin diseases significantly complicate the lives of many people and are often difficult to diagnose. Eczema and skin fungus are two conditions that are frequently confused, although they are characterized by different causes and treatment methods. Our skin is one of our largest organs, constantly exposed to external factors such as pollution, allergens, and various irritants. These factors can contribute to the development of skin problems, among which eczema and skin fungus are the most common.
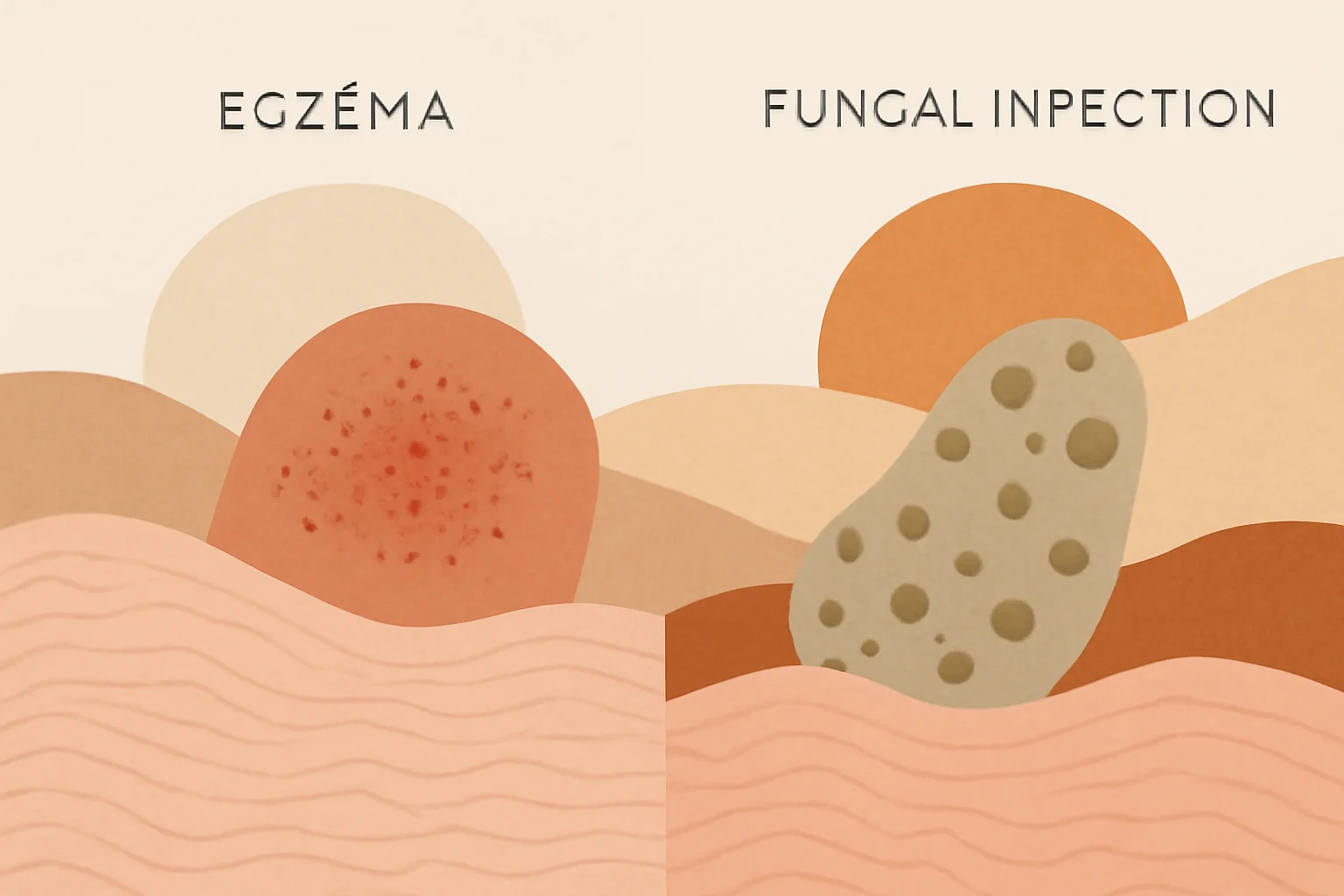
Eczema typically occurs as a result of allergic reactions, while skin fungus is the result of a fungal infection. Eczema is characterized by itching, redness, and flaking, while skin fungus most commonly causes itching, red spots, and flaking, but various colored and textured spots can also appear on the skin’s surface. Awareness of skin problems is essential, as proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial for alleviating symptoms and restoring skin health.
In this article, we will examine the characteristics, symptoms, and treatment options for eczema and skin fungus in detail to help you acquire the right information.
Characteristics and Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin disease that can manifest in various forms. The condition is often associated with allergic reactions and is a consequence of inflammatory processes in the skin. Eczema most commonly begins in childhood but can also occur in adults. Symptoms of the disease include dry skin, redness, itching, and flaking. The affected areas may have irritated and sensitive skin, causing discomfort for patients.
The causes of the disease can be diverse. Genetic predisposition, environmental factors, allergens, and irritants can all contribute to the development of eczema. Allergenic substances such as pollen, dust mites, or even certain foods can exacerbate symptoms. Additionally, stress and hormonal changes may also play a role in the flare-up of the disease.
Treatment for eczema generally focuses on alleviating symptoms. The use of moisturizing creams and topical corticosteroids can help improve the condition of the skin. It is also important to avoid irritants and properly care for the skin. Doctors often recommend medications to reduce itching so that patients can more easily tolerate the symptoms. In cases of chronic eczema, specialists may conduct further examinations to identify triggers and recommend the most appropriate treatment.
Skin Fungus: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Skin fungus, also known as mycosis, is a fungal infection that occurs on the surface of the skin. It can be caused by various types of fungi and is most commonly found in warm and moist areas of the skin, such as the armpits, groin, or between the toes. The most characteristic symptoms of skin fungus include itching, red, flaky spots, as well as skin irritation. The infection can spread through direct contact, but it can also be easily contracted in public places such as swimming pools and locker rooms.
The causes of skin fungus generally stem from conditions favorable for fungal growth, such as warm, moist environments and a weakened immune system. Those prone to fungal infections may be more susceptible to skin injuries, such as abrasions or small wounds, which allow fungi to penetrate. Fungal infections typically appear on the skin but can also affect nails and hair.
Treatment for skin fungus usually involves antifungal creams or ointments that help eliminate the fungi. Doctors often recommend that patients keep the infected areas dry and avoid wearing tight clothing, which can also contribute to the spread of the fungus. Treating skin fungus can take time, and it is important for patients to follow their doctor’s instructions for recovery.
Differences Between Eczema and Skin Fungus
Although the symptoms of eczema and skin fungus are similar in many respects, there are several essential differences between them. Eczema generally develops as a result of allergic reactions, while skin fungus originates from a fungal infection. Eczema is typically associated with dry, itchy, red spots, whereas skin fungus usually presents with wetter and flakier skin.
During diagnosis, doctors consider the condition of the skin, the symptoms, and the patient’s medical history. The diagnosis of skin fungus typically involves laboratory tests, while the diagnosis of eczema is mostly based on clinical appearance. It is important for patients to understand the differences, as treatment may also vary.
In treatment, eczema can generally be managed with topical corticosteroids and moisturizing creams, while skin fungus requires the use of antifungal medications. Treatment for eczema is often long-term, while treatment for skin fungus generally yields quicker results. In both conditions, proper skin care and avoidance of triggers are essential for prevention.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations
To prevent eczema and skin fungus, it is advisable to consider some basic lifestyle recommendations. First and foremost, it is important to regularly moisturize the skin. Dry skin is more prone to inflammation and infections, so the use of moisturizing creams is essential. Proper skin care after bathing is particularly important when the skin loses moisture.
Avoiding irritants is also crucial. Substances such as soaps, detergents, and other chemicals can exacerbate skin irritation, so it is recommended to choose skin-friendly products. The material of clothing is also an important consideration: cotton fabrics can help reduce skin irritation, while synthetic materials may increase sweating and thus the likelihood of fungal infections.
Stress management also plays an important role in maintaining skin health. Stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms, so it is worthwhile to apply relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga. A healthy diet and adequate fluid intake also contribute to the improvement of skin condition, as vitamins and minerals aid in skin regeneration.
Finally, if any skin problems arise, it is important to consult a specialist. The doctor can assist in establishing the correct diagnosis and selecting the most appropriate treatment.
Warning: This article does not constitute medical advice. If you have a health issue, please consult a doctor.

