Eczema or Skin Fungus? Symptoms and Effective Treatment Options
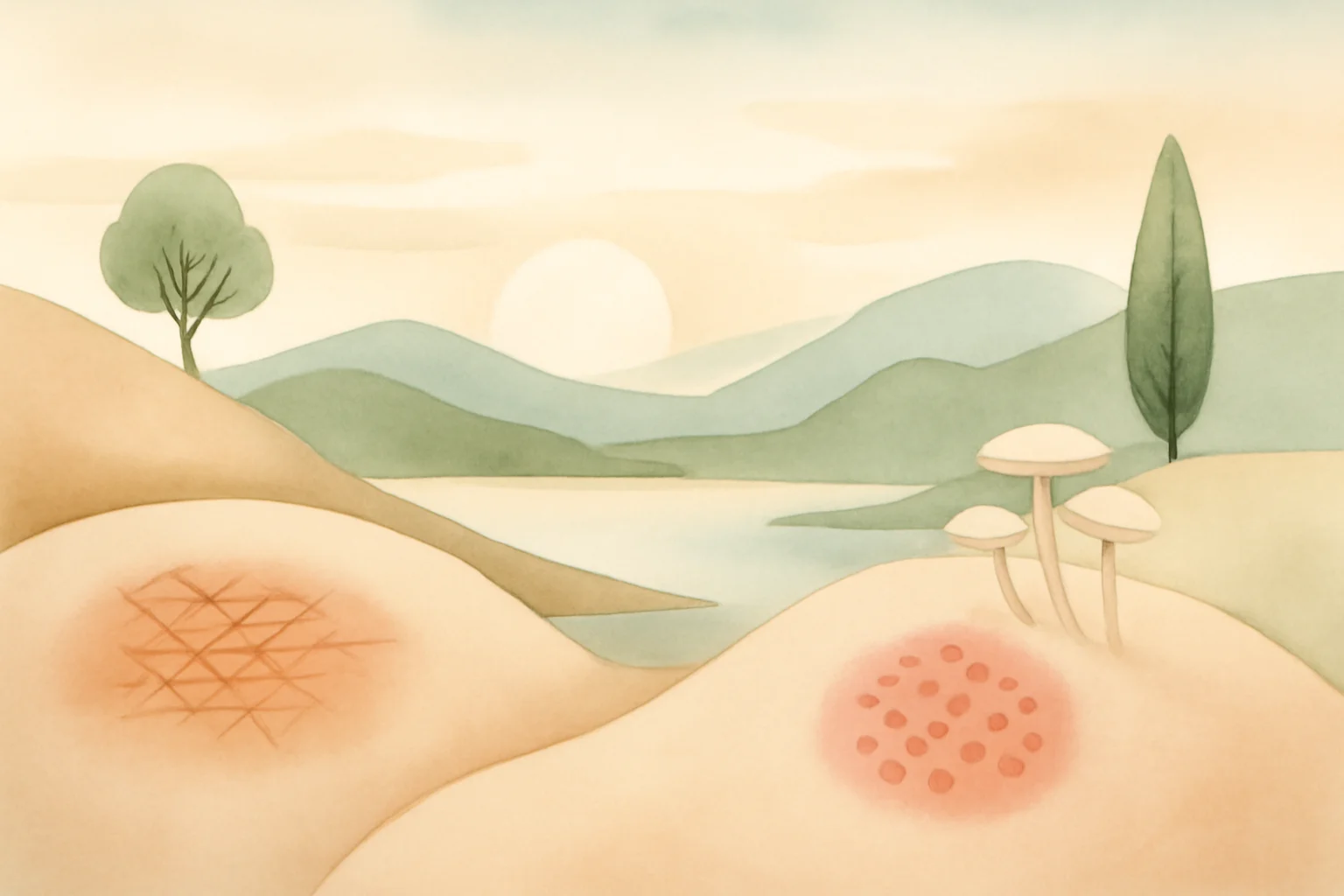
The eczema and skin fungus are two common skin problems that complicate the lives of many people. These skin diseases cause not only aesthetic but also physical discomfort. Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is often accompanied by itching, inflammation, and redness, while skin fungus, caused by a fungal infection, typically presents with blisters, peeling, and irritation. Our skin is the largest organ we have, and one of its most important functions is protection. When this protection is compromised, various problems can arise. Skin diseases not only produce physical symptoms but can also trigger psychological effects, such as anxiety or self-esteem issues.
Eczema and skin fungus can develop for various reasons, and although their symptoms may show similarities, their treatment requires different approaches. Accurate diagnosis is crucial, as incorrect treatment can not only be ineffective but can also worsen the skin condition. People often do not realize what underlying causes may be behind their skin condition, making it important to be aware of the characteristics and treatment options of the two problems.
Characteristics and Causes of Eczema
Eczema is an inflammatory condition of the skin characterized by irritation, itching, and redness. There are various forms of eczema, such as contact eczema, atopic dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis is the most common form, usually starting in childhood but can also occur in adults.
The causes of eczema can be diverse. Genetic predisposition plays an important role, as family history is often observed. Additionally, environmental factors such as pollution, allergens, and irritants can contribute to the disease’s appearance. Stress also plays a significant role in the flare-ups of eczema, as our psychological state directly affects the health of our skin.
The basis for treating eczema is moisturizing the skin and reducing inflammation. Topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, and immunomodulators are commonly used medications to alleviate symptoms. However, it is important to carry out treatment under a doctor’s supervision, as excessive use of corticosteroids can cause skin atrophy.
Recognition and Treatment of Skin Fungus
Skin fungus, also known as dermatophytosis, is a fungal infection that occurs on the skin, hair, and nails. The most common type of skin fungus is Tinea, which can appear in various forms, such as athlete’s foot, nail fungus, or body fungus. Typical symptoms of skin fungus include itching, peeling, red spots, and the appearance of blisters.
The causes of skin fungus include the presence of fungi on the skin, which thrive in particularly moist and warm environments. The infection can easily spread through direct contact, such as in swimming pools, gyms, or shared bathrooms. The state of the immune system also influences the appearance of skin fungus, making individuals with weakened immune systems more susceptible.
Treatment for skin fungus typically involves the use of topical antifungal agents, such as creams, sprays, or powders. In more severe cases, oral antifungal medications may be necessary. During treatment, it is important to maintain proper skin hygiene, avoid moist environments, and minimize direct contact to prevent the spread of infection.
Differences Between Eczema and Skin Fungus
Although both eczema and skin fungus are skin problems, there are several differences between them that are important to know for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease, while skin fungus is a fungal infection. Symptoms of eczema include dry, itchy skin that is often red and inflamed, whereas skin fungus is characterized by peeling, blistering, and itching.
The triggering causes are also different. Eczema typically develops as a result of allergic reactions and irritation, while skin fungus is an infectious process involving fungal invasion of the skin. Eczema is more prone to flare-ups triggered by stress and environmental factors, while skin fungus primarily arises from issues related to moisture and hygiene.
It is important not to confuse the two conditions, as their treatments are entirely different. Treatment for eczema generally requires skin care and the use of anti-inflammatory medications, whereas antifungal agents are necessary to combat skin fungus. An accurate diagnosis requires a medical examination, as incorrect treatment can exacerbate the skin condition.
Tips for Maintaining Skin Health
To maintain skin health, there are several steps we can take that can help prevent the development of eczema and skin fungus. One of the most important things is proper skin care. Use moisturizing creams that help retain the skin’s moisture. Hydration is especially important during the winter months when dry air and heating can make the skin drier.
Maintaining hygiene habits is also essential. Wash your hands regularly and use a separate towel for areas affected by skin problems. Avoid wearing tight, damp clothing that promotes the development of fungal infections. When using swimming pools and shared bathrooms, pay attention to adhering to hygiene rules.
Nutrition also plays a key role in skin health. Consume enough vegetables, fruits, and healthy fats that aid in skin regeneration and protection. Stress management is also important, as stress can exacerbate skin problems. Try relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga, which can help reduce stress levels.
**Warning:** This article does not constitute medical advice. In case of health issues, everyone should follow their doctor’s advice.