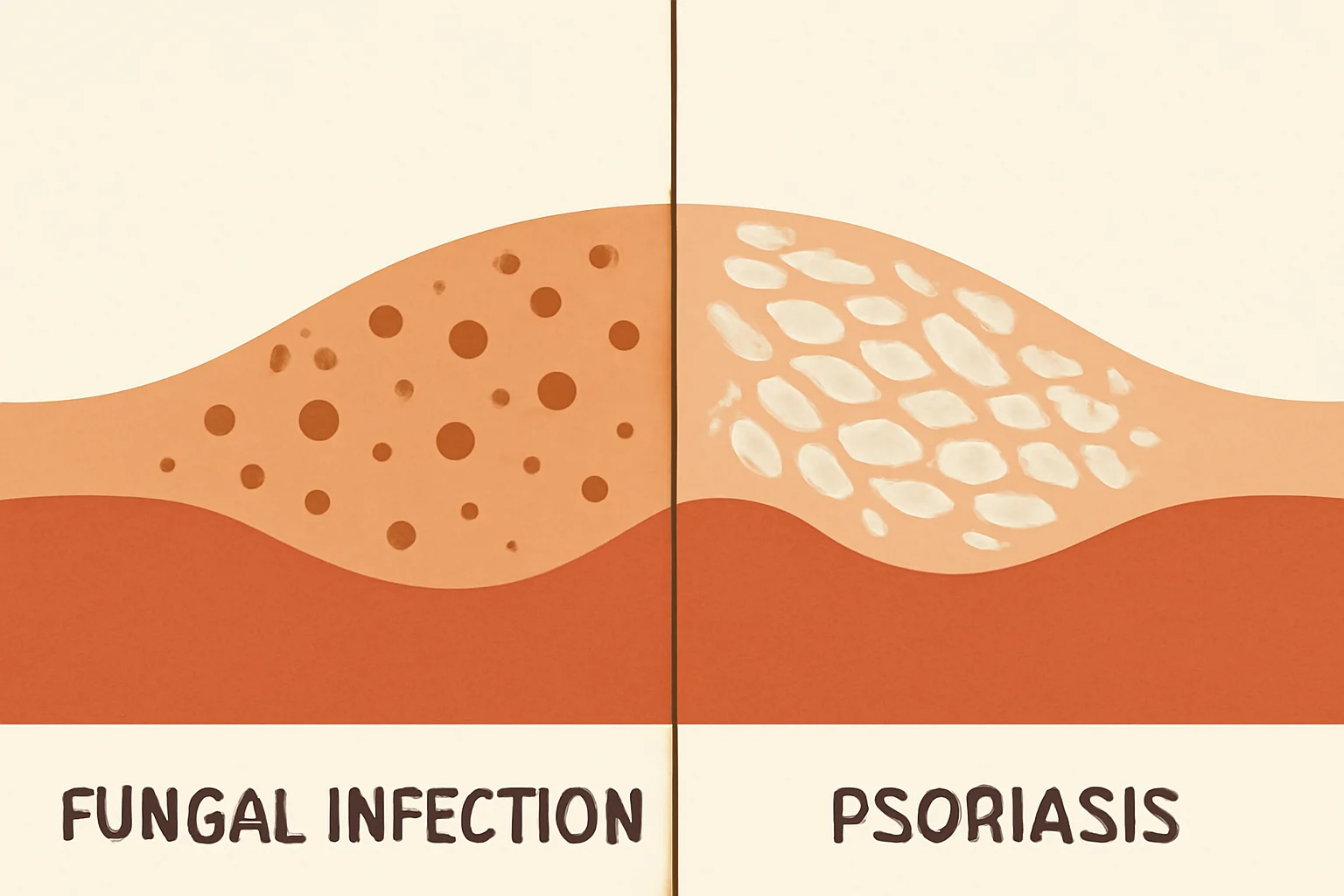
Fungal infection or psoriasis? A comparison of the two skin diseases
The skin fungus and psoriasis are two common types of skin diseases that affect many people worldwide. These disorders arise from various causes, and their appearance and symptoms can differ. Skin fungus, which is a fungal infection, typically presents with itching, scaling, and red spots, while psoriasis is an autoimmune disease characterized by the excessive proliferation of skin cells, leading to scaly, inflamed patches.
These skin problems not only cause physical discomfort but also have psychological effects, as the condition of the skin can impact many people’s self-esteem and social interactions. In the case of skin fungus, the infection often spreads easily, while psoriasis is a chronic condition that exhibits periodic flare-ups. Treatment for skin fungus usually involves the application of topical antifungal agents, while psoriasis treatment requires more complex approaches, including medications and light therapy.
The aim of this article is to examine in more detail the differences between skin fungus and psoriasis, as well as to provide useful information regarding symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Skin Fungus: Symptoms and Causes
Skin fungus, also known as mycosis, is a fungal infection affecting the skin caused by various fungi, such as dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds. The most common types of skin fungus include athlete’s foot, nail fungus, and skin fungal infections like tinea corporis. Skin fungus typically thrives in warm, moist environments, making it common among athletes, those who wear closed shoes, and individuals who frequently stay in water.
The symptoms of skin fungus vary, but they generally include itching, redness, scaling, blisters, and thickening of the skin. The infection usually affects the upper layer of the skin, but in more severe cases, it can involve deeper layers as well. It is important to maintain hygiene to prevent the spread of skin fungus, as fungi can easily be transmitted through direct contact or contact with contaminated surfaces.
Treatment for skin fungus typically involves antifungal medications, which may be applied topically or taken orally in more severe cases. To prevent skin fungus, it is recommended to keep the skin dry, remove wet clothing immediately, and wear appropriate footwear when using communal baths and swimming pools.
Psoriasis: Symptoms and Treatment Options
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that leads to the rapid proliferation of skin cells, resulting in scaly, inflamed patches. This condition is chronic and often associated with flare-ups that can be triggered by various factors such as stress, infections, or certain medications. Psoriasis is not contagious, but its symptoms can be extremely distressing and significantly impact patients’ quality of life.
The most common form of psoriasis is plaque psoriasis, which can appear on various areas of the skin, most frequently on the elbows, knees, and scalp. Symptoms include red, inflamed skin covered with silvery scales. Additionally, psoriasis can cause pain, itching, and dryness of the skin.
Treatment for psoriasis is complex and typically tailored to individual needs. Topical treatments, such as corticosteroids or vitamin D analogs, often represent the first step. In more severe cases, systemic medications like methotrexate or biologic therapies may be used. Additionally, light therapy can also be effective in treating psoriasis, as UV light can reduce the proliferation of skin cells.
The goal of psoriasis treatment is to alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups. It is important for patients to consult with their doctors about the most appropriate treatment options and to follow the prescribed treatment plan.
Differences Between Skin Fungus and Psoriasis
Although both skin fungus and psoriasis are skin problems, there are several significant differences between them. The first and foremost difference is that skin fungus is a fungal infection, while psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. This distinction affects not only the underlying causes but also the treatment options.
Skin fungus generally remains limited to the upper layer of the skin, with primary symptoms including itching and redness. In contrast, psoriasis causes much deeper skin issues, which can affect the entire immune system and have various physical and psychological effects on patients.
In treating skin fungus, antifungal agents are most commonly used, whereas psoriasis treatment is much more complex and often requires a combination of different treatment forms. Skin fungus usually responds quickly to treatment, while the treatment process for psoriasis can take longer, and symptom recurrence is common.
These differences are important for proper diagnosis and treatment, so if someone experiences a skin infection, it is crucial to consult a specialist. Accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment require medical consultation.
Prevention and Lifestyle
To prevent skin fungus and psoriasis, several steps can be taken. Maintaining proper hygiene is particularly important in the case of skin fungus, as fungal infections often develop in unsanitary conditions. Keeping the skin dry, removing wet clothing immediately, and wearing appropriate footwear when using communal baths and swimming pools can all contribute to the prevention of skin fungus.
In the case of psoriasis, prevention is more complicated, as the triggers for the disease are partly unknown. Managing stress, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and ensuring adequate sleep can all help reduce the symptoms of psoriasis. It is important for individuals with psoriasis to avoid triggers such as smoking and to pay attention to the condition of their skin.
To maintain skin health, it is advisable to regularly visit a dermatologist, who can help develop appropriate prevention and treatment strategies. Awareness and a proactive approach are the best ways to improve the quality of life for those with skin conditions.
Finally, it is important to mention that the above information does not substitute for medical advice. If you have any skin issues, always consult your doctor to receive the appropriate diagnosis and treatment.